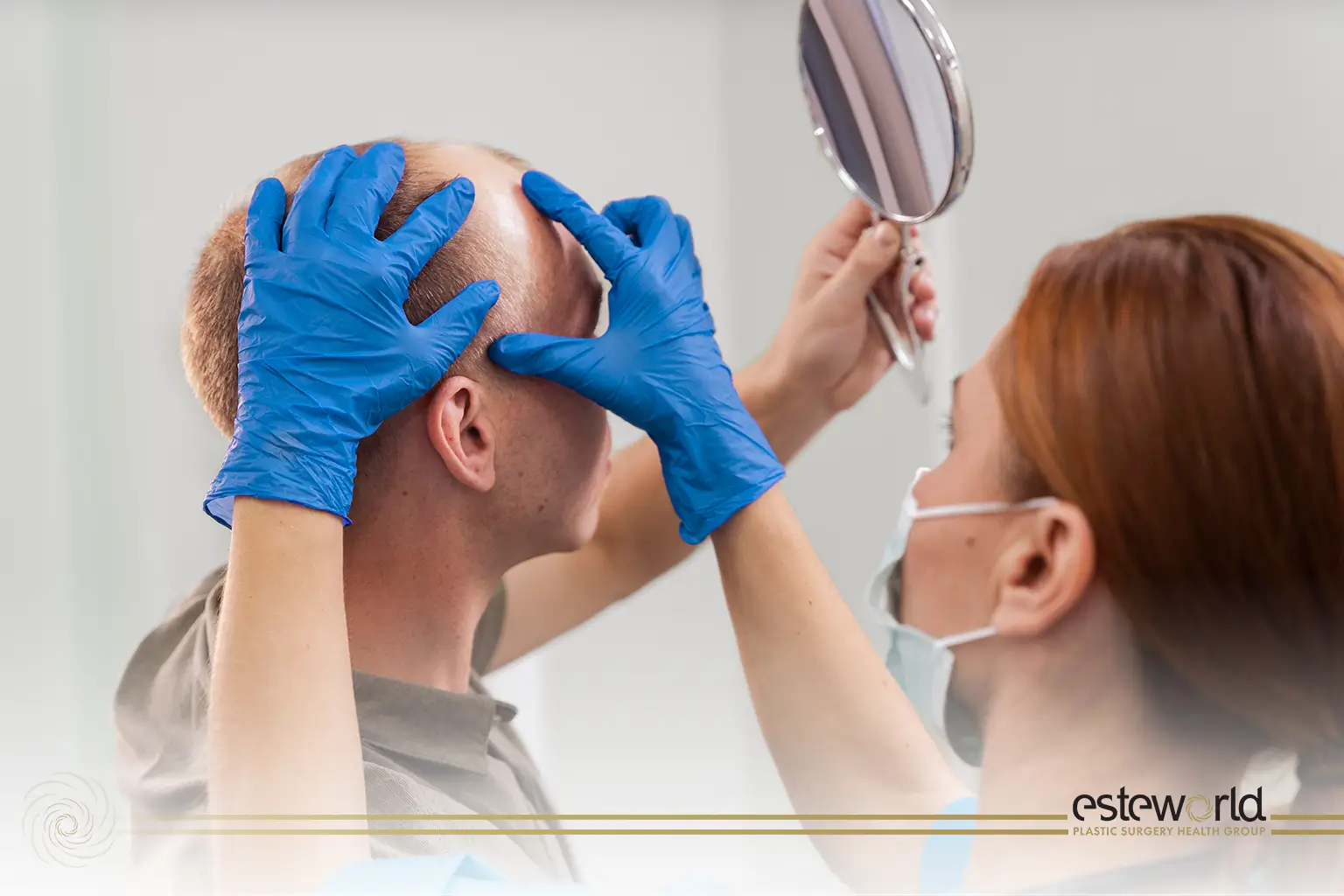
Hair loss is a common concern that can have a significant impact on the physical appearance of individuals. The fact that hair loss is often associated with genetic factors, hormonal changes and various external factors has long been the focus of research in this field. The critical role that hormones, especially androgen hormones, play in hair loss has been a subject of interest in understanding hair loss and finding effective solutions.
In this context, it is important to understand how hormonal factors play a role in understanding the origin of hair loss and evaluating the success of interventions such as hair transplantation. In this article, we will focus on the hormonal issues behind hair loss and examine the effects of hormones on hair health and hair transplant success.
What is Hair Loss? What are the Causes of Hair Loss?
Hair loss is a condition in which a person’s hair falls out in larger amounts than normal. This can occur as a result of weakened or dying hair follicles. Hair loss usually has a natural cycle of hair growth, resting and shedding, but when this cycle is disrupted or imbalanced, hair loss can occur.
- Genetic Factors (Androgenetic Alopecia): Genetic predisposition in the family is the most common cause of hair loss. It usually manifests itself as thinning in the temples and crown area in men and in the upper part of the hair in women.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes, especially imbalances in hormone levels, can cause hair loss. For example, pregnancy, menopause or hormonal disorders can lead to hair loss.
- Stress and Mental Health: Intense stress, mental health problems or severe life events can trigger or accelerate hair loss.
- Scalp Diseases: Some scalp diseases can affect the hair follicles and cause hair loss. For example, fungal infections that cause hair loss or autoimmune diseases such as lupus.
- Malnutrition: Inadequate intake of vitamins and minerals necessary for hair health can increase hair loss.
- Exposure to Chemicals: Aggressive hair care products, frequent heavy chemical treatments (e.g. perming, bleaching) can weaken the hair and cause it to fall out.
- Medical Conditions and Medications: Some medical conditions (e.g. thyroid problems) and medications can affect hair loss.
Each individual’s cause of hair loss may be different, so a personal assessment and expert opinion is important to determine the source of the problem and create the appropriate treatment plan.
What is the effect of hormones on hair health?
We have more than 100,000 hairs on our head, each growing 0.5 centimeters per month. These hairs have the ability to grow for up to six years and then enter a growth cycle. As part of this process, it is perfectly normal for between 50 and 100 hairs to fall out each day. Hormones are an important factor affecting hair health. The hair growth cycle and hair follicle activity are sensitive to hormonal changes in the body.
- Androgen Hormones and Hair Loss:
Testosterone and other androgen hormones can contribute to hair loss by causing hair follicles to shrink.
Male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) is associated with these hormones affecting the hair follicles.
- Estrogen Hormone and Hair Growth:
In women, the hormone estrogen can promote hair growth.
High estrogen levels during pregnancy can cause hair to look denser and healthier.
- Thyroid Hormones and Hair Health:
Regular levels of thyroid hormones have an impact on hair growth and hair loss.
Thyroid disorders can cause hair loss.
- Adrenal Hormones and Stress:
Cortisol, the stress hormones, can trigger hair loss when released at excessive levels.
Chronic stress can negatively affect hair health.
- Life Cycle of Hormonal Changes:
Life stages such as puberty, pregnancy, menopause can lead to changes in hormone levels, which can affect hair health.
In addition to these factors, genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, medication use and eating habits can also have an impact on hair health. The role of hormones in hair health is a complex concept and can vary depending on the individual situation. Regular health check-ups and professional counseling are important for long-term hormone balance and hair health.
Hair Transplantation and the Effect of Hormones
The effect of hormones on hair transplantation is caused by the conversion of testosterone, the main androgen hormones, into a form called dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which affects the hair follicles. This process, which is associated with genetic predisposition, can cause hair follicles to shrink and weaken, leading to hair loss. Hair transplantation is usually performed to transplant healthy hair follicles into these affected areas. Hormonal balance is important for hair transplantation to be successful and hormonal imbalances can affect the results of hair transplantation. Evaluation of hormonal levels by a specialist doctor is important for optimal results before and after hair transplantation.