Zirconium vs Porcelain Crowns: Pros,Cons and Key Differences
Dental crowns are widely used in restorative dentistry to protect damaged teeth and restore their function and appearance. Among the available options, zirconium crowns and porcelain crowns are two of the most commonly preferred materials, often compared for their durability and aesthetic results.
Although both crown types serve the same purpose, they differ in terms of material structure, strength, appearance and long-term performance. The choice between zirconium and porcelain crowns depends on factors such as the location of the tooth, aesthetic expectations and individual oral health needs.
In this article, we compare zirconium vs porcelain crowns by examining their advantages, limitations and key differences, helping you better understand which option may be more suitable for your dental treatment. The final decision should always be made in consultation with a qualified dentist following a comprehensive dental examination.
What Is a Zirconia Crown?
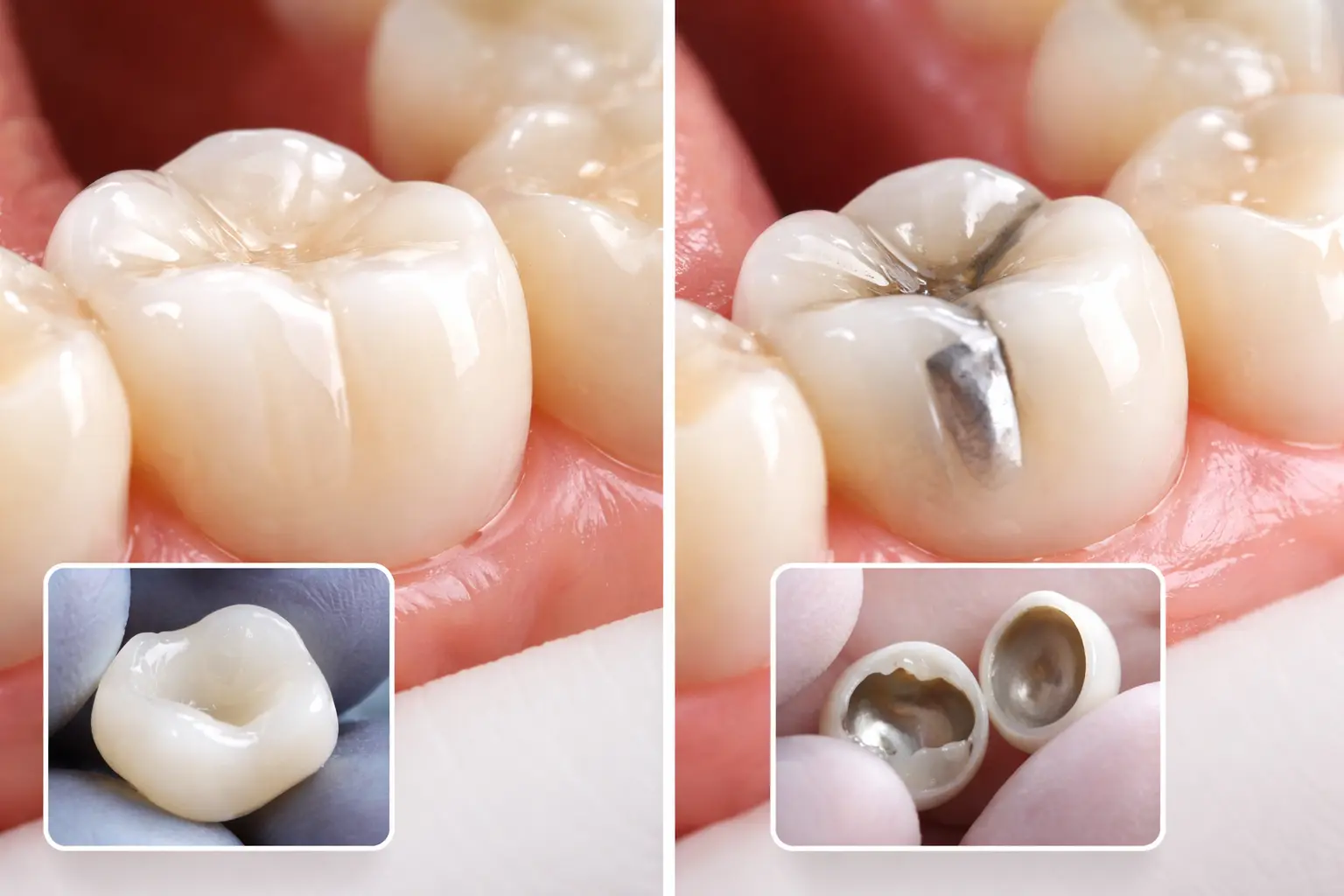
A zirconia crown is a type of dental crown made from zirconium dioxide, a strong and biocompatible ceramic material widely used in modern dentistry. Zirconia crowns are known for their high durability and resistance to fractures, making them a common choice for restoring teeth exposed to strong chewing forces, especially molars and premolars.
Due to their metal-free structure, zirconia crowns are less likely to cause allergic reactions and are generally well tolerated by gum tissues. Advances in dental technology have also improved their aesthetic quality, allowing zirconia crowns to be designed in shades that closely resemble natural teeth. This combination of strength and improved appearance has made zirconia crowns a popular option for both functional and aesthetic dental restorations.
What Is a Porcelain Crown?
A porcelain crown is a dental restoration made primarily from ceramic materials designed to closely mimic the natural appearance of teeth. Porcelain crowns are especially valued for their high aesthetic quality, as they reflect light in a way similar to natural tooth enamel. For this reason, they are commonly used for restoring front teeth where visual appearance is a primary concern.
Porcelain crowns can be fabricated as all-porcelain crowns or as porcelain-fused-to-metal crowns, depending on clinical needs. While they offer excellent colour matching and a natural-looking finish, porcelain crowns may be less resistant to heavy chewing forces compared to zirconia crowns. Therefore, their suitability often depends on the tooth’s location, bite forces and the patient’s aesthetic expectations.
What Are The Advantages Of Zirconium Crowns?
Zirconium crowns offer several advantages that make them a popular choice in modern restorative dentistry:
- High durability and strength: Zirconium crowns are highly resistant to fractures and wear, making them suitable for teeth exposed to strong chewing forces, especially molars.
- Metal-free and biocompatible structure: Their metal-free composition reduces the risk of allergic reactions and ensures good compatibility with gum tissues.
- Long-lasting performance: Due to their robust material structure, zirconium crowns are known for their long-term durability when proper oral hygiene is maintained.
- Improved gum compatibility: Zirconium crowns are less likely to cause gum irritation or dark lines around the crown margins.
- Natural-looking appearance: Advances in dental technology allow zirconium crowns to be designed in shades that closely resemble natural teeth.
- Resistance to staining: Zirconium material is less prone to staining compared to some other dental restoration materials.
What Are The Advantages Of Porcelain Crowns?
Porcelain crowns offer several advantages, particularly for patients who prioritise aesthetics and a natural-looking smile:
- Excellent aesthetic results: Porcelain crowns closely mimic the colour, translucency and light reflection of natural tooth enamel, making them ideal for visible teeth.
- Superior colour matching: They can be precisely matched to the surrounding natural teeth, helping create a seamless and harmonious appearance.
- Natural-looking translucency: Porcelain material allows light to pass through in a way similar to natural teeth, enhancing overall smile aesthetics.
- Suitable for front teeth restorations: Due to their visual qualities, porcelain crowns are commonly preferred for anterior teeth where appearance is critical.
- Customisable design: Porcelain crowns can be shaped and layered to meet individual aesthetic needs and smile design goals.
- Proven clinical use: Porcelain materials have been used in dentistry for many years, providing a well-documented history of successful clinical outcomes.
What Is The Healing Process Like For Zirconium Crowns vs Porcelain Crowns?
The healing process after zirconium crowns and porcelain crowns is generally similar, as both procedures follow the same basic clinical steps. However, individual experiences may vary depending on gum health, tooth preparation and overall oral hygiene.
After the crown placement, mild sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures may occur for a short period. This sensitivity usually decreases as the tooth and surrounding tissues adapt to the new restoration. Temporary crowns may be used before the final crown placement, during which the gums continue to heal and stabilise.
Zirconium crowns are often well tolerated by gum tissues due to their biocompatible and metal-free structure. This may contribute to reduced gum irritation and smoother soft tissue adaptation in some patients. Porcelain crowns also support healthy healing, although metal-supported porcelain crowns may occasionally cause minor gum sensitivity in certain cases.
In both cases, maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding hard foods during the initial days and following the dentist’s aftercare instructions play a crucial role in the healing process. Regular dental check-ups help ensure that the crown fits properly and that the surrounding tissues remain healthy.
What Are The Differences Between Zirconium Crowns And Porcelain Crowns?
| Feature | Zirconium Crowns | Porcelain Crowns |
| Material structure | Made from zirconium dioxide, a high-strength ceramic material | Made from ceramic materials designed mainly for aesthetics |
| Durability | Highly resistant to fractures and heavy chewing forces | Durable, but may be more prone to chipping under strong pressure |
| Aesthetic appearance | Improved aesthetics, slightly less translucent in some cases | Excellent translucency and natural tooth-like appearance |
| Gum compatibility | Metal-free and highly biocompatible with gum tissues | Generally gum-friendly, metal-supported types may cause minor sensitivity |
| Preferred tooth location | Commonly used for molars and premolars | Frequently preferred for front teeth |
| Resistance to wear | High resistance to long-term wear | Moderate resistance compared to zirconium |
| Risk of gum discolouration | Very low due to metal-free structure | Slight risk in porcelain-fused-to-metal crowns |
| Longevity | Long-lasting with proper oral care | Long-lasting with proper oral care |
Which One Should I Choose: Zirconium Crowns or Porcelain Crowns?
Choosing between zirconium crowns and porcelain crowns depends on individual dental needs rather than a single “best” option. Both crown types are effective, but they are suited to different clinical and aesthetic situations.
Zirconium crowns are often recommended for patients who prioritise strength and durability. They are particularly suitable for back teeth, such as molars and premolars, where chewing forces are stronger. Patients who grind their teeth or require a long-lasting restoration may also benefit from zirconium crowns due to their high resistance to wear and fractures.
Porcelain crowns, on the other hand, are generally preferred when aesthetics are the primary concern. Their natural translucency and superior colour matching make them an ideal choice for front teeth that are visible when smiling or speaking. Porcelain crowns are well suited for patients who value a highly natural appearance and harmonious smile design.
Ultimately, the most suitable crown type should be determined after a detailed dental examination. Factors such as tooth position, bite force, gum health and aesthetic expectations all play a role in this decision. Consulting an experienced dentist is essential to ensure a treatment plan that meets both functional and aesthetic goals.